Unveiling the Hidden Culprit with Health issues: What Triggers Inflammation
- Posted/Updated: March 9th, 2026
Many health professional will tell you that the most common ailment preceding serious disease will invariably be inflammation.
Inflammation is a reaction to injury, infection, trauma or an underlying health condition such as cancer, autoimmune conditions, infections and obesity.
When damage to our body occurs. our immune system sends in inflammatory mediators which signal to the body that it needs healing. If it cannot heal, prolonged inflammation, most often results in chronic pain.
Chronic inflammation can have diverse and serious impact on overall health and well-being.
Inflammation is a complex biological immune system response involving various processes in the body, including 1) Initiation, 2) Response, 3) Resolution.
In 2004, The Time Magazine (Feb 23, 2004 issue) referred to Inflammation as the Silent killer. It stated: “Inflammation is the body’s first defense against infection, but when it goes awry, it can lead to heart attacks, colon cancer, Alzheimer’s, and a host of other diseases”.
Inflammation is a self-limiting process, and once the threat is neutralized and tissue repair begins, the inflammatory response is gradually dampened and resolved.
"By targeting inflammation, we have the potential to not only treat diseases but also prevent them from occurring in the first place." --- Dr. Rangan Chatterjee
"The link between inflammation and disease is undeniable; addressing inflammation should be a primary focus in both preventive and therapeutic medicine." --- Dr. Aviva Romm
Inflammation typically begins with the recognition of harmful stimuli, such as pathogens, damaged cells, or irritants, by the body's immune system. This recognition triggers the release of signaling molecules called cytokines and the activation of immune cells, such as macrophages and neutrophils, which are deployed to the site of injury or infection.
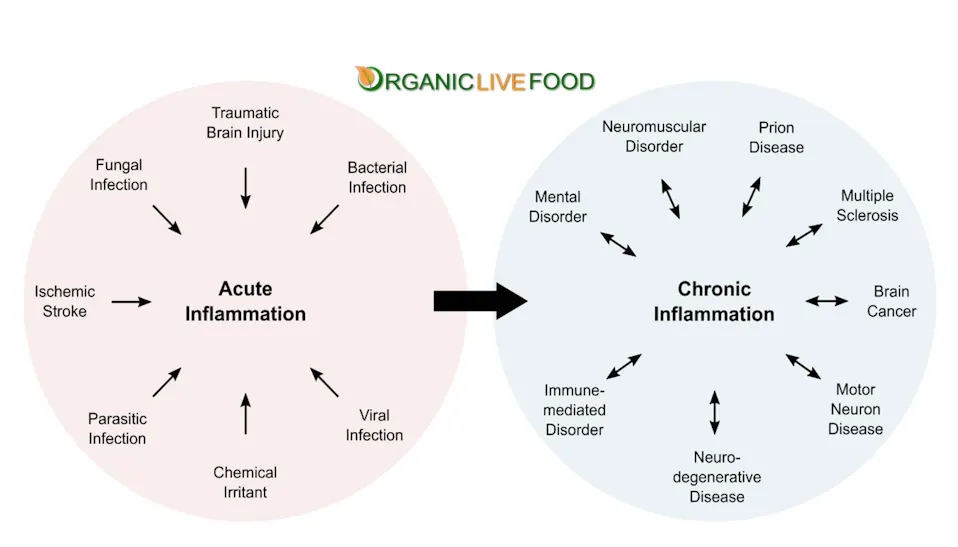
- What is Inflammation?
- Inflammation is the body's way of signaling the immune system to heal and repair damaged tissues. It involves a complex cascade of chemical processes that increase blood flow to the affected area, resulting in redness, swelling, heat, and pain. While acute inflammation is a short-term response, chronic inflammation can persist for prolonged periods, causing tissue damage and contributing to various diseases.
- What are the Causes of Inflammation?
- Inflammation can be triggered by a variety of factors, including certain foods, lifestyle habits, and underlying health conditions. Understanding these triggers is crucial for managing and reducing inflammation effectively. Some common causes of inflammation include:1) Unhealthy Diet; 2) Sedentary Lifestyle; 3) Smoking; 4) Stress; 5) Obesity; 6) Infection; among others.
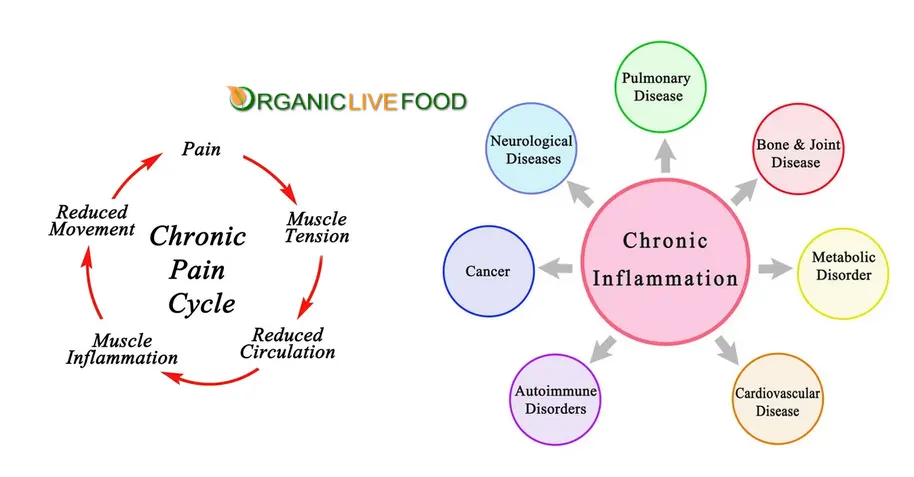
- What is the Impact of Chronic Inflammation?
- Prolonged inflammation can have serious implications for overall health. It has been linked to various chronic conditions, including cardiovascular disease, diabetes, arthritis, and even certain types of cancer. By understanding the impact of chronic inflammation, we can take proactive steps to manage and reduce it.
- Why is it Important to Manage and Reduce Inflammation?
- Managing inflammation is crucial for maintaining optimal health and well-being. By adopting an anti-inflammatory lifestyle, which includes following a balanced and nutritious diet, engaging in regular exercise, managing stress levels, getting adequate sleep, and avoiding harmful habits, we can effectively reduce chronic inflammation and promote overall wellness.
- Why does Sedentary Lifestyle cause Inflammation?
- Prolonged sitting or a lack of physical activity can lead to chronic inflammation. Regular exercise, such as walking, swimming, or cycling, helps reduce inflammation by improving circulation and boosting the immune system. Incorporate at least 30 minutes of moderate-intensity exercise into your daily routine to keep inflammation in check.
- Poor Sleep Patterns, can it Cause Inflammation?
- Insufficient or poor-quality sleep can cause the body to produce higher levels of inflammatory proteins. Aim for 7-9 hours of uninterrupted sleep each night to promote healing and reduce inflammation. Establish a regular sleep schedule and create a soothing bedtime routine to improve the quality and duration of your sleep.
- Does Chronic Stress Cause Inflammation?
- Stress triggers the release of stress hormones like cortisol, which can contribute to chronic inflammation. Practice stress-reducing techniques such as meditation, deep breathing exercises, or engaging in hobbies that bring you joy. Seeking support from friends, family, or a therapist can also help in managing stress and preventing inflammation.
- Can Inflammation be Caused by Environmental Toxins?
- Yes. Indeed, Exposure to environmental toxins, such as air pollution, pesticides, and chemicals, can trigger inflammation in the body. Minimize exposure to these toxins by ensuring proper ventilation in your living spaces, using natural cleaning products, and consuming organic foods whenever possible.
- How does Smoking and Excessive Alcohol Consumption Cause Inflammation?
- Cigarette smoke contains numerous harmful chemicals that can trigger inflammation throughout the body. Smoking damages blood vessels, weakens the immune system, and increases the risk of developing chronic diseases. Quitting smoking or avoiding exposure to secondhand smoke is crucial for reducing inflammation and improving overall health.
- Alcohol abuse can lead to inflammation in the liver and other organs. It weakens the immune system and disrupts the body's natural inflammatory response. Limit your alcohol intake to moderate levels or consider abstaining from alcohol altogether to reduce inflammation and protect your organs.
- Can Poor Hygiene Cause Inflammation?
- Absolutley, it can. Neglecting personal hygiene practices can result in infections, which can cause inflammation. Proper handwashing, oral hygiene, and regular bathing help prevent the spread of harmful bacteria and reduce inflammation. Incorporate good hygiene habits into your daily routine to promote a healthy inflammatory response.
Foods that Trigger Inflammation
Inflammation occurs when the body's immune system responds to injury, infection, or other harmful stimuli.
One factor that can significantly influence inflammation is our diet.
Certain foods have been found to trigger and exacerbate inflammation in the body. By recognizing these foods and making dietary changes, we can work towards reducing inflammation and promoting overall well-being.
- Processed Foods
- Processed foods, including packaged snacks, fast food, and sugary beverages, are known culprits for promoting inflammation. These foods often contain high levels of unhealthy fats, refined carbohydrates, and added sugars, which can lead to inflammation within the body. Opting for whole, unprocessed foods is a better choice to reduce inflammation.
- Saturated and Trans Fats
- Foods that are high in saturated and trans fats, such as red meat, fried foods, and baked goods, can trigger inflammation. These fats promote the production of inflammatory chemicals called cytokines in the body. Choosing healthier fats like olive oil, avocados, and nuts can help reduce inflammation.
- Sugar and Artificial Sweeteners
- Consuming excessive amounts of sugar and artificial sweeteners can lead to inflammation. These substances can stimulate the release of inflammatory messengers in the body. Limiting the intake of sugary treats, sodas, and artificial sweeteners like aspartame and sucralose is vital for managing inflammation.
- Refined Grains
- Refined grains, such as white bread, white rice, and pasta, undergo processing that strips away essential nutrients and fiber. These foods have a high glycemic index and can cause a rapid spike in blood sugar levels, leading to increased inflammation. Opt for whole grains like quinoa, brown rice, and whole wheat bread instead.
- Dairy Products
- Dairy products, especially those derived from cow's milk, contain a protein called casein, which can trigger inflammation in some individuals. People who are sensitive or intolerant to dairy may experience increased inflammation symptoms. Consider alternative milk options like almond milk, soy milk, or oat milk.
- Gluten
- Gluten is a protein found in wheat, barley, and rye. For individuals with gluten sensitivity or celiac disease, consuming gluten can lead to inflammation in the gut and other parts of the body. It is essential to avoid gluten-containing products and opt for gluten-free alternatives like quinoa, rice, and corn.
- Alcohol
- Excessive alcohol consumption has been linked to increased inflammation in the body. Alcohol can disrupt the normal functioning of the immune system, leading to chronic inflammation. Moderation is crucial when it comes to alcohol consumption to minimize the risk of inflammation-related health issues.
- Artificial Additives
- Artificial additives, such as preservatives, flavor enhancers, and food coloring, can trigger inflammation and allergic responses in some individuals. These additives are commonly found in processed foods and beverages. Reading food labels and choosing natural, additive-free options can help reduce inflammation.
Understanding and managing inflammatory responses in the body is crucial for maintaining optimal health and well-being.
It's important to understand the various factors that can trigger inflammation, including specific foods, habits, and disorders. by identifying and avoiding these triggers, individuals can take proactive steps towards reducing inflammation and mitigating its negative impact on overall health.
There are also practical strategies for managing inflammatory responses, such as incorporating anti-inflammatory foods into our diet, adopting healthier habits, and seeking appropriate medical treatment for underlying disorders.
You can also adopt a holistic approach and making informed choices, we have the power to promote a healthier and inflammation-free lifestyle, enhancing our overall quality of life.
Remember, knowledge is the key, and with the right tools and understanding, you CAN effectively reduce or eliminate inflammation and experience the benefits of improved well-being.


