Nervous and muscular systems are critical in our body and play a vital role in maintaining our overall well-being, allowing us to move, think, and experience the world around us and protect our body.
By incorporating healthy lifestyle practices such as regular exercise, proper nutrition, stress management techniques, and adequate rest into our daily routines, we can ensure optimal functioning of these vital systems.
Keeping the nervous and muscular systems healthy involves a combination of lifestyle habits and proactive measures. Regular physical activity, including aerobic exercises, strength training, and flexibility exercises, supports both systems by promoting blood flow, strengthening muscles, and enhancing nerve function.
Adequate sleep is crucial for nerve repair and muscle recovery. A balanced diet rich in nutrients like omega-3 fatty acids, antioxidants, vitamins, and minerals supports nerve health and muscle function.
Our body's nervous system serves as the master communication network between all the organs and maintain control of all the functions. It consists of two main components: the central nervous system (CNS) and the peripheral nervous system (PNS. The CNS comprises the brain and spinal cord, while the PNS includes all other nerves throughout the body.
Managing stress through relaxation techniques such as meditation, deep breathing exercises, or yoga can reduce tension in muscles and support overall nervous system health.
Avoiding harmful substances like excessive alcohol and drugs helps protect nerve cells and maintain muscle function. Regular check-ups with healthcare providers can ensure early detection and management of any neurological or muscular issues, contributing to long-term health and well-being.
The nervous system performs several vital functions that are essential for our survival:
Neurons are the building blocks of communication. They are specialized cells responsible for transmitting electrical signals throughout our bodies. They consist of three main parts:
Neurotransmitters are the chemical messengers.
Neurons communicate with each other through chemical messengers called neurotransmitters. These molecules transmit signals across tiny gaps called synapses, allowing information to flow seamlessly.
The brain and spinal cord form the central nervous system (CNS).
The peripheral nervous system (PNS), also known as 'extending communication', comprises all nerves outside of the CNS. It can be further divided into two subdivisions:
Maintaining a healthy nervous system is vital for overall well-being. Here are some tips to optimize its functioning:
- Stay active, as regular exercise promotes blood flow to the brain, enhancing cognitive function.
- Get adequate sleep, because sufficient sleep supports optimal brain health and promotes memory consolidation.
- Eat a nutrient-rich diet, for instance, consuming omega-3 fatty acids, antioxidants, vitamins, and minerals nourishes nerve cells.
- Manage stress, do yoga, or whatever you can to rest as chronic stress can damage neurons over time; incorporate stress management techniques like meditation or yoga into your routine.
- Challenge your brain, for cognitive health, through engaging in mentally stimulating activities and sharpening cognitive abilities.
The muscular system consists of hundreds of muscles that enable movement throughout our bodies. From flexing our biceps to walking or even blinking an eye—our muscles work tirelessly every day.
What role does the nervous system play in muscle function?
The nervous system controls muscle function by sending electrical signals from the brain or spinal cord to muscles. These signals trigger muscle contractions, enabling movement.
Can exercise improve nervous system health?
Yes, regular exercise supports overall nervous system health by enhancing blood flow to the brain and promoting neuroplasticity—the brain's ability to reorganize itself.
How do neurotransmitters influence mood and emotions?
Neurotransmitters like serotonin, dopamine, and norepinephrine play a crucial role in regulating mood and emotions. Imbalances in these neurotransmitters can contribute to conditions like depression or anxiety.
Does age affect the muscular system's performance?
As we age, our muscles naturally tend to weaken due to a decrease in muscle mass. However, engaging in regular physical activity can help slow down this process and maintain muscular strength.
Is it possible to enhance muscle growth without supplements?
Absolutely! A well-balanced diet rich in lean proteins, such as poultry or legumes, provides ample nutrients for muscle growth. Supplements are not necessary but may be beneficial for some individuals with specific dietary needs.
How does the brain coordinate voluntary and involuntary muscle movements?
Voluntary muscle movements are controlled by the cerebral cortex, which sends signals via motor neurons to initiate and regulate movement. Involuntary muscle movements, such as those involved in maintaining posture and balance, are coordinated by brain regions like the cerebellum and brainstem, which receive sensory input and adjust muscle activity accordingly to maintain equilibrium and smooth coordination of movements.
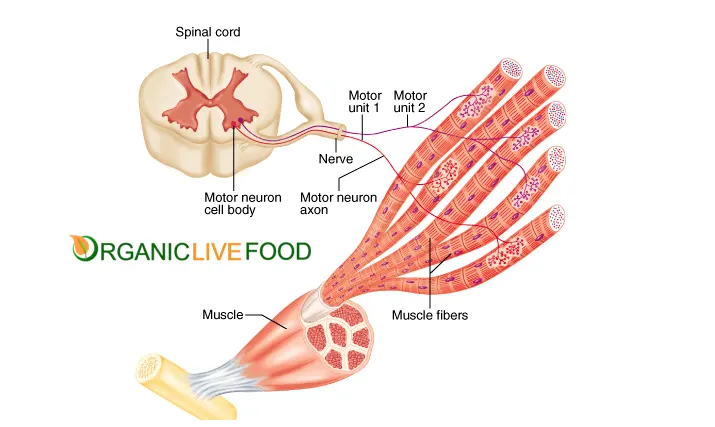
What is the structure and function of the neuromuscular junction?
The neuromuscular junction is the site where a motor neuron meets a muscle fiber, allowing for communication between the nervous system and muscles. When an action potential reaches the neuromuscular junction, it triggers the release of neurotransmitter acetylcholine, which binds to receptors on the muscle fiber, leading to depolarization of the muscle cell membrane and initiation of muscle contraction. This process ensures precise control of muscle activity by the nervous system.
How does muscle contraction occur at the cellular level?
Muscle contraction involves a complex series of events at the cellular level. When a motor neuron stimulates a muscle fiber, it triggers the release of calcium ions from the sarcoplasmic reticulum. These ions bind to proteins within the muscle fiber, causing a change in shape that exposes binding sites on actin filaments. Myosin heads then attach to these sites, forming cross-bridges and pulling the actin filaments towards the center of the sarcomere, resulting in muscle contraction.
