The key factors that contribute to inflammation in the body can be linked to diet, habits, diseases and disorders. Inflammation in our body's defence kicking in to protect, and by nurthuring it, we can help ourselves by having a stronger immune system that ensures living a healthier, inflammation-free life.
Inflammation can have diverse and serious impact on overall health and well-being.
Inflammation is a fast trigger of immune system response involving various processes in the body, including 1) Initiation, 2) Response, 3) Resolution.
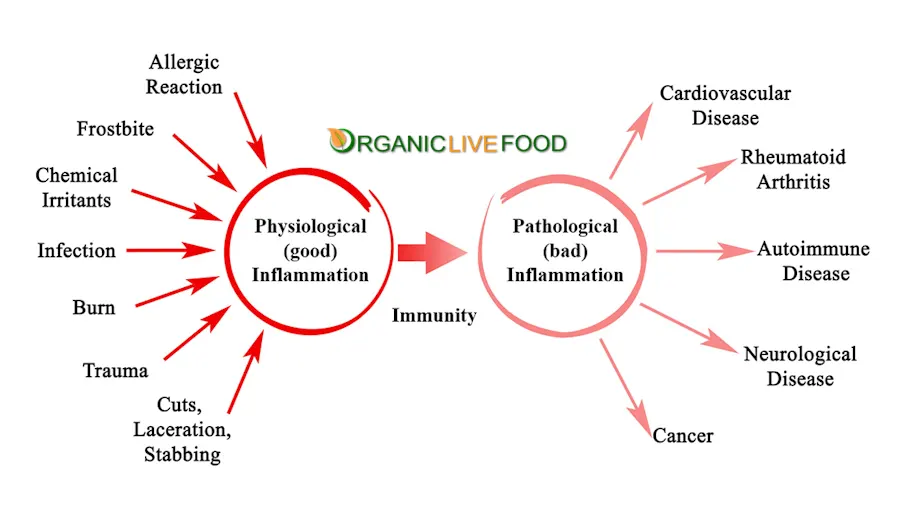
This natural response by the body's immune system to injury or infection, involves a complex interplay of chemical signals and immune cells that work together to protect and heal the affected area. So while it is necessary for healing, excessive or prolonged inflammation can lead to discomfort and tissue damage.
Once immune cells arrive at the site of inflammation, they work to eliminate the threat and repair any damage. This involves processes such as phagocytosis, where immune cells engulf and digest pathogens or debris, and the release of inflammatory mediators to recruit additional immune cells to the area. Blood vessels near the site may dilate to increase blood flow, leading to redness and warmth, and become more permeable, allowing immune cells and fluid to enter tissues, resulting in swelling.
Inflammation is a sophisticated interaction between chemical signals and immune cells that collaborate to safeguard and promote healing in the affected area. Failure to properly resolve inflammation can lead to chronic inflammation, which is associated with various diseases and conditions.
"Inflammation is the body's way of signaling that something is wrong, but when it becomes chronic, it can wreak havoc on our health. Inflammation isn't just a response to injury; it's a driving force behind many of the diseases that plague modern society." --- Dr. Frank Lipman
"Chronic inflammation disrupts the body's delicate balance and sets the stage for disease to take hold." --- Dr. Joel Kahn
Inflammation is a natural response of the immune system to protect the body from harmful stimuli.
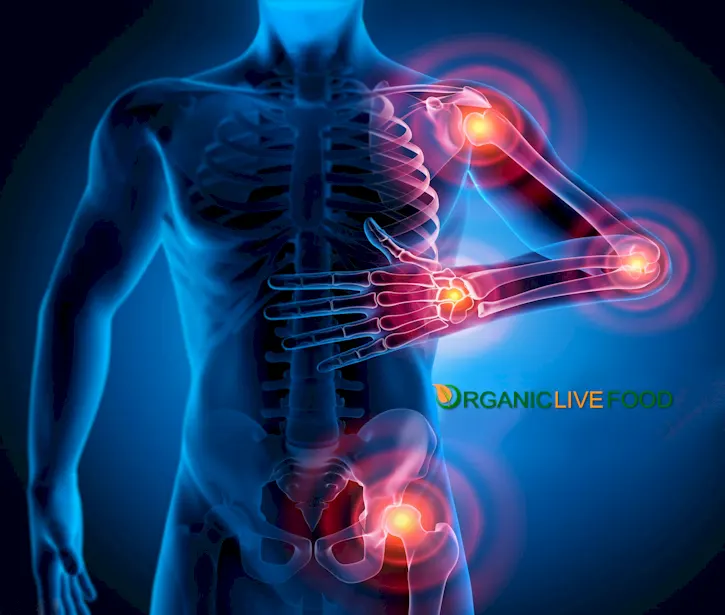
When an injury or infection happens, prostaglandins are produced as part of a chain reaction that leads to localized swelling, redness, and discomfort. Prostaglandins are responsible for promoting pain, swelling, and fever during the inflammatory process.
However, certain disorders can disrupt this delicate balance, leading to chronic inflammation that can have detrimental effects on overall health. Sometimes prolonged exposure to un-treated inflammation causes the underlying diseases, or make it exasperated.
Some common disorders that have been linked to triggering inflammation in the body include:
Certain foods have been found to promote inflammation in the body. These include:
- Processed Foods: Foods high in refined carbohydrates, trans fats, and additives can contribute to inflammation.
- Sugar: Excessive consumption of sugary foods and beverages can lead to chronic inflammation.
- Saturated Fats: Foods rich in saturated fats, such as red meat and full-fat dairy, have been linked to increased inflammation.
- Vegetable Oils: Certain vegetable oils, like soybean, corn, and sunflower oils, contain high levels of omega-6 fatty acids, which can lead to inflammation when consumed in excess.
Our lifestyle habits can also play a role in triggering inflammation, for instance::
- Lack of Exercise: Sedentary behavior can contribute to chronic low-grade inflammation in the body.
- Smoking: Smoking has been linked to increased inflammation and can worsen existing inflammatory conditions.
- Stress: Chronic stress can lead to an overactive immune response and chronic inflammation.
Several disorders are associated with inflammation. These include:
- Arthritis: Various forms of arthritis, such as rheumatoid arthritis and osteoarthritis, involve inflammation in the joints.
- Inflammatory Bowel Disease: Conditions like Crohn's disease and ulcerative colitis cause chronic inflammation in the digestive tract.
- Autoimmune Diseases: Disorders like lupus, multiple sclerosis, and psoriasis are characterized by an overactive immune system and chronic inflammation.
Managing inflammation is crucial for overall health and well-being. Here's what you can do::
- Anti-inflammatory Diet: Focus on consuming a variety of fruits, vegetables, whole grains, fatty fish, and healthy fats like olive oil.
- Regular Exercise: Engage in moderate-intensity exercise for at least 30 minutes most days of the week.
- Stress Management: Practice relaxation techniques like meditation, deep breathing, and yoga to reduce stress levels.
- Get Enough Sleep: Aim for 7-9 hours of quality sleep each night to support the body's healing processes.